平均感知机分词
13 Aug 2018 | NLP |感知机其实就是一个二分类算法,通过y = sign(wx+b)公式进行计算,来判断类别。
平均感知机是在每次训练时,对于正确地样本,则权重值加1;对于正确的样本,则权重值加1;对于错误的样本,则权重值减1。
下面提到的是基于基于结构化平均感知机的分词器Java实现这篇文章中的信息。它的代码实现集成在了HanLP中,你可以点击查看。
首先,需要从句子中抽取特征,Hanlp中定义的特征模板(或规则)是,一共7个特征:
Ci-1 #前一个词
Ci #当前词
Ci+1 #后一个词
Ci-2/Ci-1 #前两个词与前一个词
Ci-1/Ci #前一个词与当前词
Ci/Ci+1 #当前词与后一个词
Ci+1/Ci+2 #后一个词与后两个词
抽取特征部分源码,更多细节,你可以查看完整源码:
/**
* sentence:当前的句子
* featureMap:一个TreeMap,用于保存所有特征
* position:句子的index,即此时处理的哪一个字符
*/
protected int[] extractFeature(String sentence, FeatureMap featureMap, int position)
{
List<Integer> featureVec = new LinkedList<Integer>();
char pre2Char = position >= 2 ? sentence.charAt(position - 2) : CHAR_BEGIN;//前两个词
char preChar = position >= 1 ? sentence.charAt(position - 1) : CHAR_BEGIN;//前一个词
char curChar = sentence.charAt(position);//当前词
char nextChar = position < sentence.length() - 1 ? sentence.charAt(position + 1) : CHAR_END;//后一个词
char next2Char = position < sentence.length() - 2 ? sentence.charAt(position + 2) : CHAR_END;//后两个词
StringBuilder sbFeature = new StringBuilder();
sbFeature.delete(0, sbFeature.length());
sbFeature.append(preChar).append('1');
addFeature(sbFeature, featureVec, featureMap);//第一个特征,前一个词
sbFeature.delete(0, sbFeature.length());
sbFeature.append(curChar).append('2');
addFeature(sbFeature, featureVec, featureMap);//第二个特征,当前词
sbFeature.delete(0, sbFeature.length());
sbFeature.append(nextChar).append('3');
addFeature(sbFeature, featureVec, featureMap);//第三个特征,后一个词
//char bigram feature
sbFeature.delete(0, sbFeature.length());
sbFeature.append(pre2Char).append("/").append(preChar).append('4');
addFeature(sbFeature, featureVec, featureMap);//第四个特征,前两个词与前一个词
sbFeature.delete(0, sbFeature.length());
sbFeature.append(preChar).append("/").append(curChar).append('5');
addFeature(sbFeature, featureVec, featureMap);//第五个特征,前一个词与当前词
sbFeature.delete(0, sbFeature.length());
sbFeature.append(curChar).append("/").append(nextChar).append('6');
addFeature(sbFeature, featureVec, featureMap);//第六个特征,当前词与后一个词
sbFeature.delete(0, sbFeature.length());
sbFeature.append(nextChar).append("/").append(next2Char).append('7');
addFeature(sbFeature, featureVec, featureMap);//第七个特征,后一个词与后两个词
return toFeatureArray(featureVec);//所有特征转为一个数组
}
比如,一个句子是:商品与服务,假设当前处理的词是与,那么与的特征就是:
品
与
服
商品
品与
与服
服务
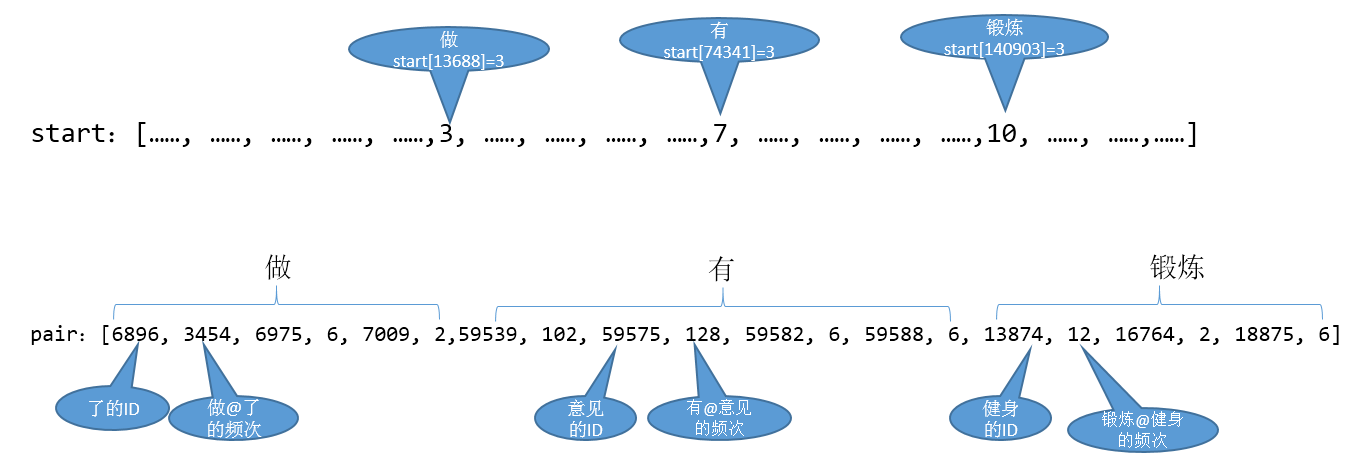
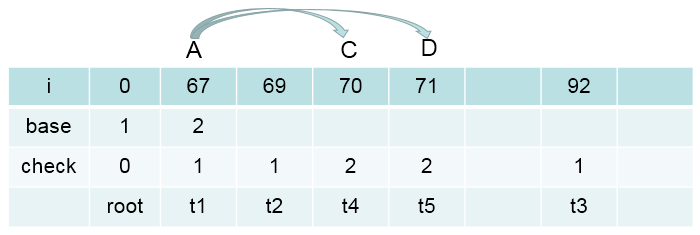
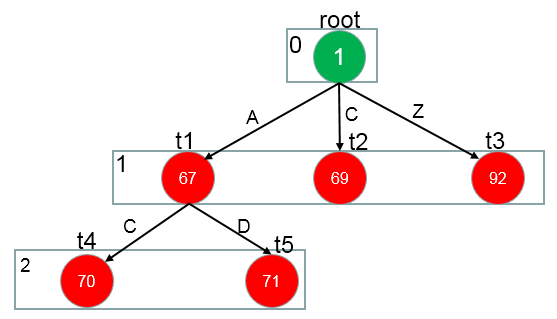
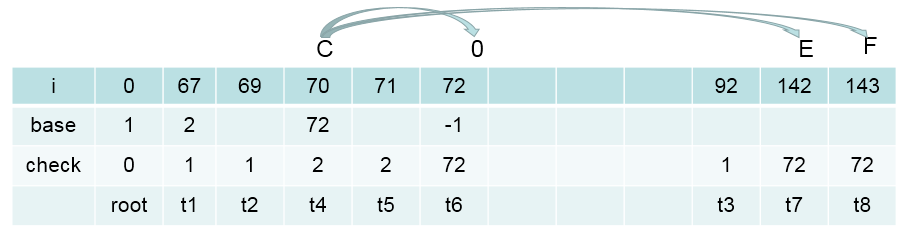
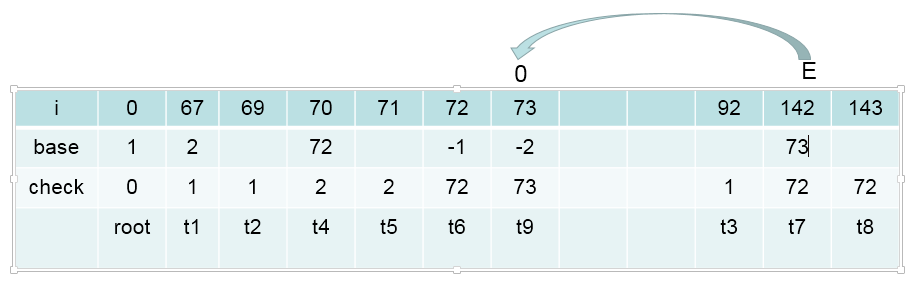
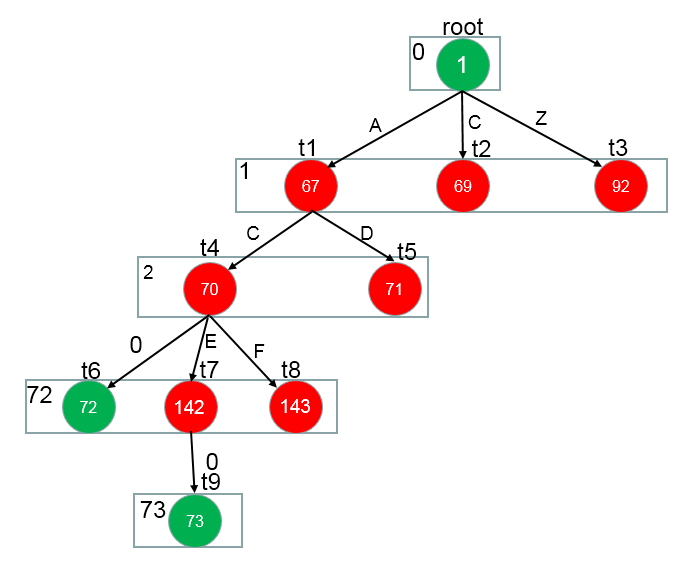
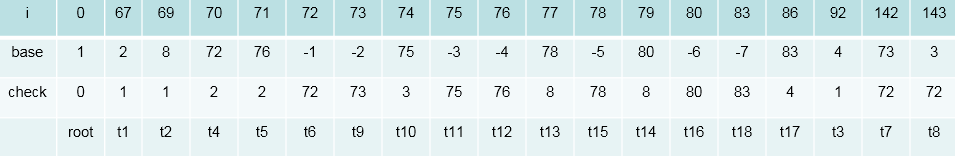
画个图表示下(特征数值化的表示方法,可以在源码中找到。其实就是每次添加特征时,当前map的大小作为此时特征id)
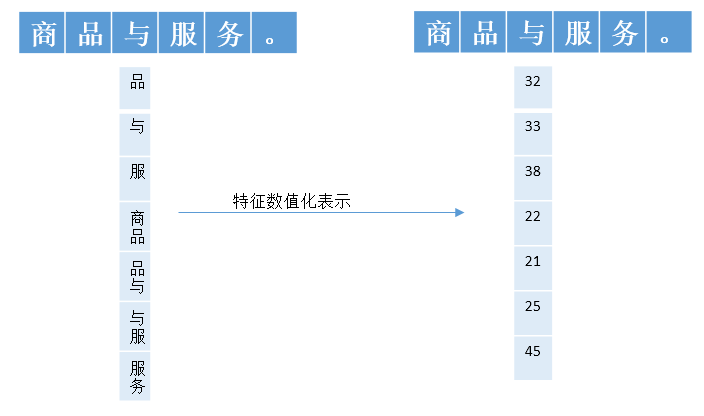
一共7个特征,在实际处理时,需要把上面的特征转化为数值,便于计算机处理。 按照定义的特征模板,对所有的语料中的句子,句子中的字符进行处理,以得到全部的特征。
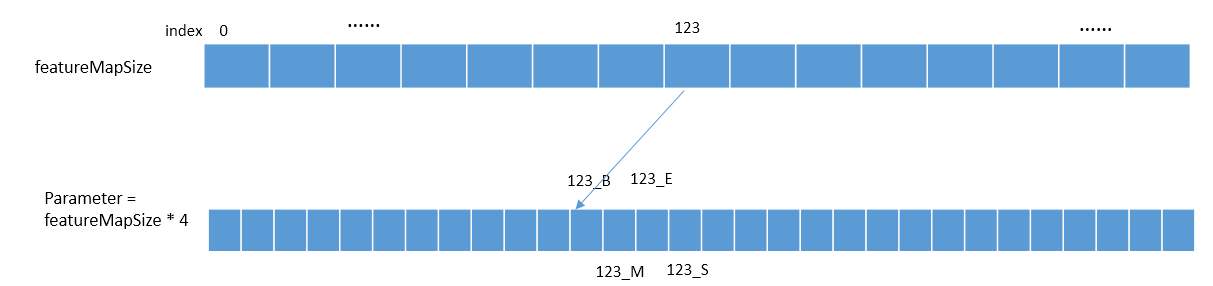
抽取的所有特征都对应一个特征参数。现在,我们是在处理分词任务,用B,M,E,S表示,那么我们总共要训练的特征参数就是featureMapSize * 4,即每一个特征对B,M,E,S的影响。
训练的部分代码:
// 加载训练语料
TagSet tagSet = createTagSet();
MutableFeatureMap mutableFeatureMap = new MutableFeatureMap(tagSet);
ConsoleLogger logger = new ConsoleLogger();
logger.start("开始加载训练集...\n");
Instance[] instances = loadTrainInstances(trainingFile, mutableFeatureMap);//所有句子实例
tagSet.lock();
logger.finish("\n加载完毕,实例一共%d句,特征总数%d\n", instances.length, mutableFeatureMap.size() * tagSet.size());
// 开始训练
ImmutableFeatureMap immutableFeatureMap = new ImmutableFeatureMap(mutableFeatureMap.featureIdMap, tagSet);
mutableFeatureMap = null;
double[] accuracy = null;
AveragedPerceptron model;
model = new AveragedPerceptron(immutableFeatureMap);
final double[] total = new double[model.parameter.length];
final int[] timestamp = new int[model.parameter.length];
int current = 0;//每次迭代,每个句子就加一,记录时间戳
for (int iter = 1; iter <= maxIteration; iter++)
{
Utility.shuffleArray(instances);//数据随机化
for (Instance instance : instances)
{
++current;
int[] guessLabel = new int[instance.length()];
model.viterbiDecode(instance, guessLabel);//用不断更新的模型去做预测
for (int i = 0; i < instance.length(); i++)
{
int[] featureVector = instance.getFeatureAt(i);//一个字符的特征向量
int[] goldFeature = new int[featureVector.length];//正确的特征
int[] predFeature = new int[featureVector.length];//预测的特征
for (int j = 0; j < featureVector.length - 1; j++)//7个自定义特征
{
goldFeature[j] = featureVector[j] * tagSet.size() + instance.tagArray[i];//实际特征+实际标签作为特征,方便后面的权重特征更新
predFeature[j] = featureVector[j] * tagSet.size() + guessLabel[i];//实际特征+预测标签作为特征,方便后面的权重特征更新
}
goldFeature[featureVector.length - 1] = (i == 0 ? tagSet.bosId() : instance.tagArray[i - 1]) * tagSet.size() + instance.tagArray[i];//正确的转移特征
predFeature[featureVector.length - 1] = (i == 0 ? tagSet.bosId() : guessLabel[i - 1]) * tagSet.size() + guessLabel[i];//预测的转移特征
model.update(goldFeature, predFeature, total, timestamp, current);//更新权重值
}
}
}
/*******权重值更新update*******/
/**
* 根据答案和预测更新参数
*
* @param goldIndex 预测正确的特征函数
* @param predictIndex 命中的特征函数
*/
public void update(int[] goldIndex, int[] predictIndex, double[] total, int[] timestamp, int current)
{
for (int i = 0; i < goldIndex.length; ++i)
{
if (goldIndex[i] == predictIndex[i])
continue;
else
{
update(goldIndex[i], 1, total, timestamp, current);//正确预测,权重加1
if (predictIndex[i] >= 0 && predictIndex[i] < parameter.length)
update(predictIndex[i], -1, total, timestamp, current);//错误预测,权重减1
else
{
throw new IllegalArgumentException("更新参数时传入了非法的下标");
}
}
}
}
/*******实际权重值更新update*******/
/**
* 根据答案和预测更新参数
*
* @param index 特征向量的下标
* @param value 更新量
* @param total 权值向量总和
* @param timestamp 每个权值上次更新的时间戳
* @param current 当前时间戳
*/
private void update(int index, float value, double[] total, int[] timestamp, int current)
{
int passed = current - timestamp[index];//距离index上次更新已经过去多少个时刻了
total[index] += passed * parameter[index];
parameter[index] += value;//特征权重更新
timestamp[index] = current;
}
/*******模型预测,使用维特比算法预测一个字符是{B,M,E,S}哪一标签*******/
/**
* 维特比解码
*
* @param instance 实例
* @param guessLabel 输出标签
* @return
*/
public double viterbiDecode(Instance instance, int[] guessLabel)
{
final int[] allLabel = featureMap.allLabels();//所有标签
final int bos = featureMap.bosTag();//标签集合大小
final int sentenceLength = instance.tagArray.length;//句子长度
final int labelSize = allLabel.length;//标签集合大小
int[][] preMatrix = new int[sentenceLength][labelSize];//转态转移矩阵
double[][] scoreMatrix = new double[2][labelSize];//滚动数组,记录上一次分数和这一次分数
for (int i = 0; i < sentenceLength; i++)
{
int _i = i & 1;
int _i_1 = 1 - _i;//用于滚动数组
int[] allFeature = instance.getFeatureAt(i);//一个字符的所有特征
final int transitionFeatureIndex = allFeature.length - 1;
if (0 == i)
{
allFeature[transitionFeatureIndex] = bos;
for (int j = 0; j < allLabel.length; j++)
{
preMatrix[0][j] = j;
double score = score(allFeature, j);
scoreMatrix[0][j] = score;
}
}
else
{
//每一个状态转移到哪一个更好
for (int curLabel = 0; curLabel < allLabel.length; curLabel++)
{
double maxScore = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
//上一次的状态0,1,2,3 哪一个转移curLabel状态更好
for (int preLabel = 0; preLabel < allLabel.length; preLabel++)
{
allFeature[transitionFeatureIndex] = preLabel;//转移特征
double score = score(allFeature, curLabel);//当前标签的词特征权值和作为分数,以此表示当前词特征作为某一种标签的概率
double curScore = scoreMatrix[_i_1][preLabel] + score;//分数累加
if (maxScore < curScore)//分数越大越好
{
maxScore = curScore;
preMatrix[i][curLabel] = preLabel;//上一次preLabel状态转移到curLabe状态更好
scoreMatrix[_i][curLabel] = maxScore;
}
}
}
}
}
int maxIndex = 0;
double maxScore = scoreMatrix[(sentenceLength - 1) & 1][0];
//找出最后一次的最大值和索引
for (int index = 1; index < allLabel.length; index++)
{
if (maxScore < scoreMatrix[(sentenceLength - 1) & 1][index])
{
maxIndex = index;
maxScore = scoreMatrix[(sentenceLength - 1) & 1][index];
}
}
//反向回溯,预测标签
for (int i = sentenceLength - 1; i >= 0; --i)
{
guessLabel[i] = allLabel[maxIndex];
maxIndex = preMatrix[i][maxIndex];
}
return maxScore;
}
上面的部分源码是主要的训练过程,实际分词的时候,用训练好的特征权重值作为参数,维特比算法找出每个字符最有可能的{B,M,E,S}中的哪一个值。
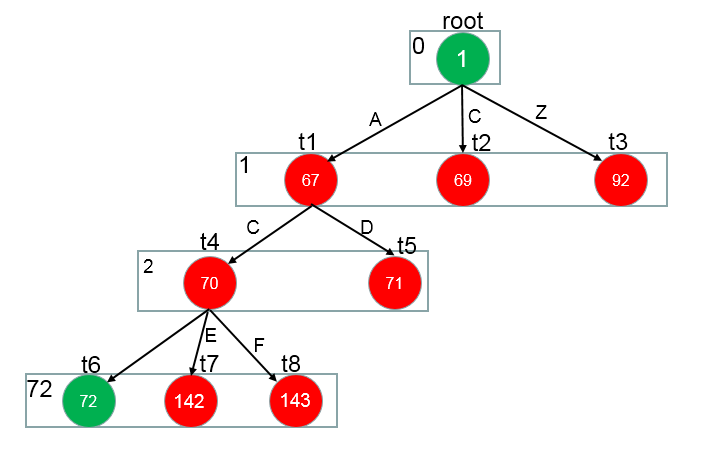
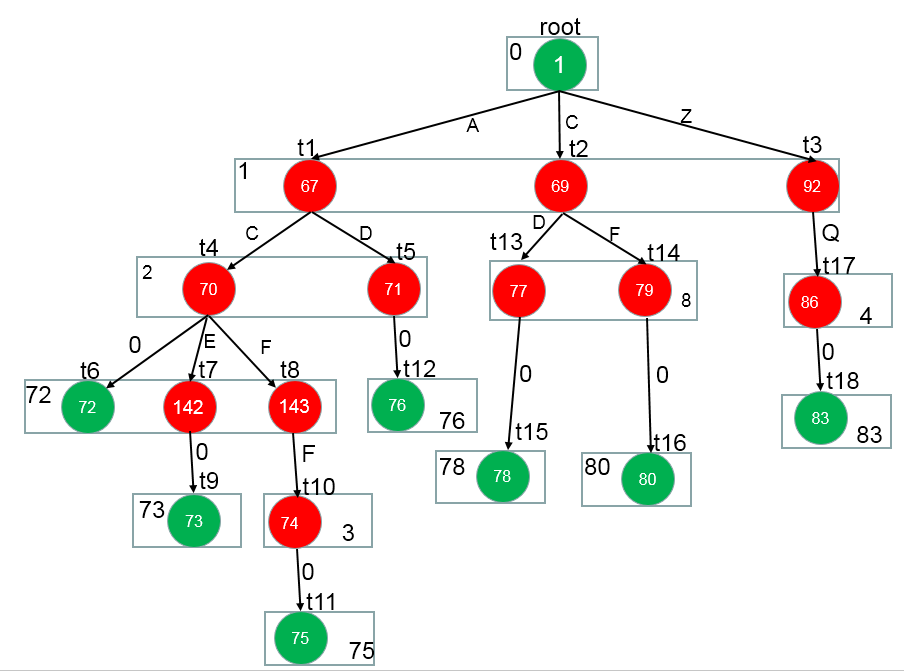
为了便于理解上述流程,我自己画了一个图:
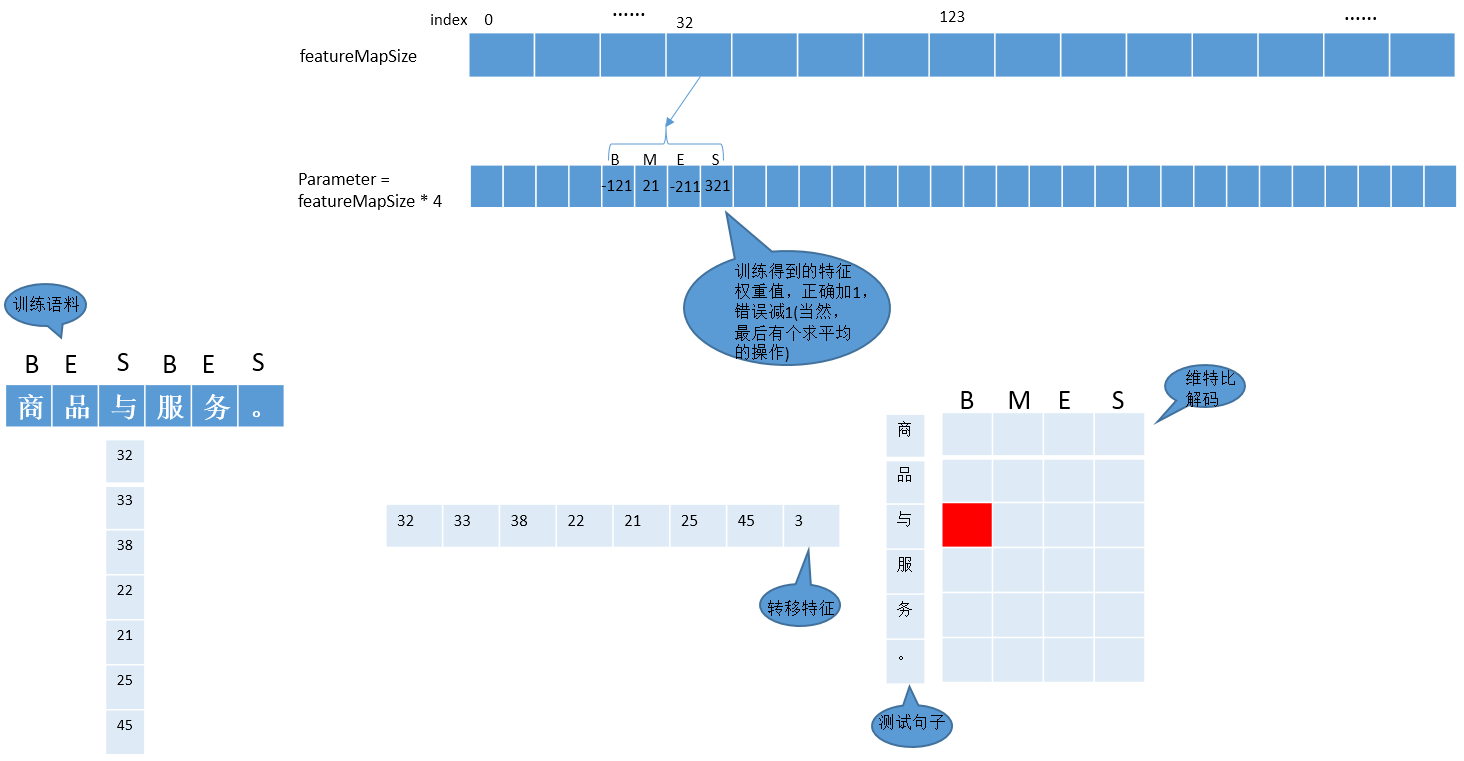
上面红色位置的表示应该是{B,M,E,S}中的哪一个值,计算的方法就是源码中的score()函数:
计算特征中与B相关的所有特征权重值:
score_B = para[32_B] + para[33_B]+...+para[3_B]
按照上述一样的方法计算score_M,score_E,score_S
然后取最大值,作为红色位置中的值