最大熵模型推导与实现
14 Oct 2018 | NLP |熵是对信息的不确定性进行度量,熵值越大,不确定性就越大。当我们对某些事情进行预测的时候,除了给定的约束条件之外,没有其他可用信息了,那么如何对未知的事情进行预测,才是合理的呢?
最大熵原理认为
在所有可能的模型中,熵最大的模型是最好的模型。
在满足约束条件时,对所有可能的结果进行等概率预测,即结果符合均匀分布(均匀分布的熵是最大的)。这种预测方式是合情合理的,因为没有其他可用信息了,每种结果都有可能出现,而且等概率。
最大熵模型是由以下条件概率分布表示的分类模型。
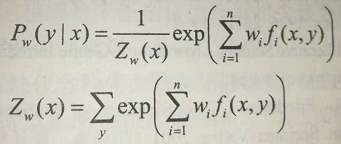
其中,Z(x)是规范化因子,f(x,y)是特征函数,w为特征权重。
Note: 最大熵原理的数学推导请参考李航《统计学习方法》
最大熵模型的优化算法
GIS(通用迭代尺度法)和IIS(改进迭代尺度法):


Note:图片来源:peghoty
最大熵模型推导
熵

最大熵模型的学习

最大熵模型p(y|x)

对偶函数极大化

目标函数最优化

极大似然估计

最大熵模型算法实现:
import javafx.util.Pair;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.*;
/**
* 最大熵的简明实现,提供训练与预测接口,训练算法采用GIS训练算法
* @author hankcs
*/
public class MaxEnt
{
/**
* 样本数据集
*/
List<Instance> instanceList = new ArrayList<Instance>();
/**
* 特征列表,来自所有事件的统计结果
*/
List<Feature> featureList = new ArrayList<Feature>();
/**
* 每个特征的出现次数
*/
List<Integer> featureCountList = new ArrayList<Integer>();
/**
* 事件(类别)集
*/
List<String> labels = new ArrayList<String>();
/**
* 每个特征函数的权重
*/
double[] weight;
/**
* 一个事件最多一共有多少种特征
*/
int C;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException
{
String path = "F:\\MaxEnt-master\\data\\train.txt";
MaxEnt maxEnt = new MaxEnt();
maxEnt.loadData(path);
maxEnt.train(200);
List<String> fieldList = new ArrayList<String>();
fieldList.add("Sunny"); // 假如天晴
fieldList.add("Humid"); // 并且湿润
Pair<String, Double>[] result = maxEnt.predict(fieldList); // 预测出门和自宅的概率各是多少
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(result));
}
/**
* 加载数据,并且创建如下域
* featureList:特征函数的list
* featureCountList:与特征函数一一对应的,特征函数出现的次数
* instanceList:样本数据list
* labels:类别list
*
* @param path
* @throws IOException
*/
public void loadData(String path) throws IOException
{
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(new File(path)));
String line = br.readLine();
while (line != null)
{
String[] segs = line.split("\\s");
String label = segs[0];
List<String> fieldList = new ArrayList<String>();
for (int i = 1; i < segs.length; ++i)
{
fieldList.add(segs[i]);
Feature feature = new Feature(label, segs[i]);
int index = featureList.indexOf(feature);
//记录特征与特征次数
if (index == -1)
{
featureList.add(feature);
featureCountList.add(1);
}
else
{
featureCountList.set(index, featureCountList.get(index) + 1);
}
}
if (fieldList.size() > C) C = fieldList.size();
Instance instance = new Instance(label, fieldList);//一个样本
instanceList.add(instance);
if (labels.indexOf(label) == -1) labels.add(label);
line = br.readLine();
}
}
/**
* 训练模型
* @param maxIt 最大迭代次数
*/
public void train(int maxIt)
{
int size = featureList.size();
weight = new double[size]; // 特征权重
double[] empiricalE = new double[size]; // 经验期望
double[] modelE = new double[size]; // 模型期望
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i)
{
empiricalE[i] = (double) featureCountList.get(i) / instanceList.size();
}
double[] lastWeight = new double[weight.length]; // 上次迭代的权重
for (int i = 0; i < maxIt; ++i)
{
computeModeE(modelE);
//GIS 算法 ,参数更新
for (int w = 0; w < weight.length; w++)
{
lastWeight[w] = weight[w];
weight[w] += 1.0 / C * Math.log(empiricalE[w] / modelE[w]);
}
if (checkConvergence(lastWeight, weight)) break;
}
}
/**
* 预测类别
* @param fieldList
* @return
*/
public Pair<String, Double>[] predict(List<String> fieldList)
{
double[] prob = calProb(fieldList);
Pair<String, Double>[] pairResult = new Pair[prob.length];
for (int i = 0; i < prob.length; ++i)
{
pairResult[i] = new Pair<String, Double>(labels.get(i), prob[i]);
}
return pairResult;
}
/**
* 检查是否收敛
* @param w1
* @param w2
* @return 是否收敛
*/
public boolean checkConvergence(double[] w1, double[] w2)
{
for (int i = 0; i < w1.length; ++i)
{
if (Math.abs(w1[i] - w2[i]) >= 0.01) // 收敛阀值0.01可自行调整
return false;
}
return true;
}
/**
* 计算模型期望,即在当前的特征函数的权重下,计算特征函数的模型期望值。
* @param modelE 储存空间,应当事先分配好内存(之所以不return一个modelE是为了避免重复分配内存)
*/
public void computeModeE(double[] modelE)
{
Arrays.fill(modelE, 0.0f);
for (int i = 0; i < instanceList.size(); ++i)
{
List<String> fieldList = instanceList.get(i).fieldList;
//计算当前样本X对应所有类别的概率
double[] pro = calProb(fieldList);
for (int j = 0; j < fieldList.size(); j++)
{
for (int k = 0; k < labels.size(); k++)
{
Feature feature = new Feature(labels.get(k), fieldList.get(j));
int index = featureList.indexOf(feature);
if (index != -1)
modelE[index] += pro[k] * (1.0 / instanceList.size());
}
}
}
}
/**
* 计算p(y|x),此时的x指的是instance里的field
* @param fieldList 实例的特征列表
* @return 该实例属于每个类别的概率
*/
public double[] calProb(List<String> fieldList)
{
double[] p = new double[labels.size()];
double sum = 0; // 正则化因子,保证概率和为1
for (int i = 0; i < labels.size(); ++i)
{
double weightSum = 0;
//根据公式进行计算p(y|x)
for (String field : fieldList)
{
Feature feature = new Feature(labels.get(i), field);
int index = featureList.indexOf(feature);
if (index != -1)
weightSum += weight[index];
}
p[i] = Math.exp(weightSum);
sum += p[i];
}
for (int i = 0; i < p.length; ++i)
{
p[i] /= sum;
}
return p;
}
/**
* 一个观测实例,包含事件和时间发生的环境
*/
class Instance
{
/**
* 事件(类别),如Outdoor
*/
String label;
/**
* 事件发生的环境集合,如[Sunny, Happy]
*/
List<String> fieldList = new ArrayList<String>();
public Instance(String label, List<String> fieldList)
{
this.label = label;
this.fieldList = fieldList;
}
}
/**
* 特征(二值函数)
*/
class Feature
{
/**
* 事件,如Outdoor
*/
String label;
/**
* 事件发生的环境,如Sunny
*/
String value;
/**
* 特征函数
* @param label 类别
* @param value 环境
*/
public Feature(String label, String value)
{
this.label = label;
this.value = value;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj)
{
Feature feature = (Feature) obj;
if (this.label.equals(feature.label) && this.value.equals(feature.value))
return true;
return false;
}
@Override
public String toString()
{
return "[" + label + ", " + value + "]";
}
}
}
参考文献:
- 李航 - 统计学习方法
- 最大熵学习笔记(五)最优化算法
- 最大熵的Java实现