关系抽取论文解读-Relation classification via convolutional deep neural network
21 Jul 2018 | relation-extraction |关系抽取是从一个句子中判断出这个句子里面两个实体之间的关系。
比如给定句子:
1 "The system as described above has its greatest application in an arrayed <e1>configuration</e1> of antenna <e2>elements</e2>."
Component-Whole(e2,e1)
Comment: Not a collection: there is structure here, organisation.
上面的句子是数据集 SemEval 2010 Task 8 数据集 中的一个训练集的实际样本,1表示第一条句子,<e1>configuration</e1> 是指明了实体一, <e2>elements</e2>是指明了实体二,Component-Whole(e2,e1)表明了两个实体之间的关系是Component-Whole关系。Comment是对句子的一些描述信息。
数据集SemEval 2010 Task 8中关系是9种,为了区别正反(Cause-Effect(e1,e2)与Cause-Effect(e2,e1)看作是两种关系)和其他(other,有些句子中的实体关系不是给定的关系)一共是19种关系:
(1) Cause-Effect
(2) Instrument-Agency
(3) Product-Producer
(4) Content-Container
(5) Entity-Origin
(6) Entity-Destination
(7) Component-Whole
(8) Member-Collection
(9) Message-Topic
那么我们要根据训练集训练出的模型对句子中的关系进行预测。
A few days before the service, Tom Burris had thrown into Karen's <e1>casket</e1> his wedding <e2>ring</e2>.
上面就是测试例子,请给出两个实体之间的关系。这就是我们要做的关系抽取,现在的关系抽取都是有监督的关系抽取,还有半监督的,还有无监督的(开放域的实体关系抽取),这在深度学习中还是研究热点。
接下来就进入正文:
Relation classification via convolutional deep neural network
【Zeng, D & Liu, K & Lai, S & Zhou, G & Zhao, J. (2014). Relation classification via convolutional deep neural network. the 25th International Conference on Computational Linguistics: Technical Papers. 2335-2344. 】这篇文章使用了比较经典的CNN的结构,包含了池化层,进行关系抽取。
论文成果:
- 1.不使用复杂的NLP(不需要词性标记与句法分析)进行关系抽取
- 2.使用位置特征来表示距离
- 3.在SemEval-2010 Task 8数据集进行了实验,与传统方法进行了对比
网络架构:
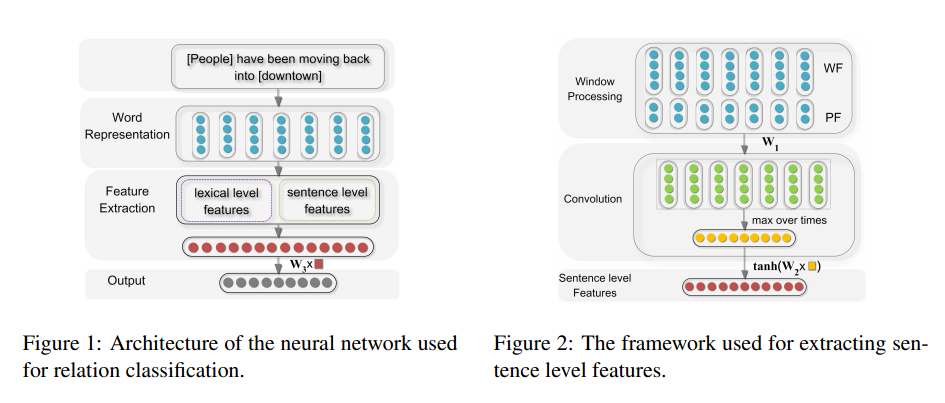 首先获取全部词构成一个字典,然后把句子中的词转化为对应的ID(一个整数表示),接着再把这些词表示为一个向量,并统一设置句子长度,那么一个句子就被转化为98 x 50 的向量矩阵。
首先获取全部词构成一个字典,然后把句子中的词转化为对应的ID(一个整数表示),接着再把这些词表示为一个向量,并统一设置句子长度,那么一个句子就被转化为98 x 50 的向量矩阵。
原始训练文件:
1"The system as described above has its greatest application in an arrayed <e1>configuration</e1> of antenna <e2>elements</e2>."
Component-Whole(e2,e1)
Comment: Not a collection: there is structure here, organisation.
处理后的文件:
3 12 12 15 15 the system as described above has its greatest application in an arrayed configuration of antenna elements
3 表示关系 Component-Whole(e2,e1)
12 表示实体1的位置
15 表示实体2的位置
一个句子中的所有词用数字表示:
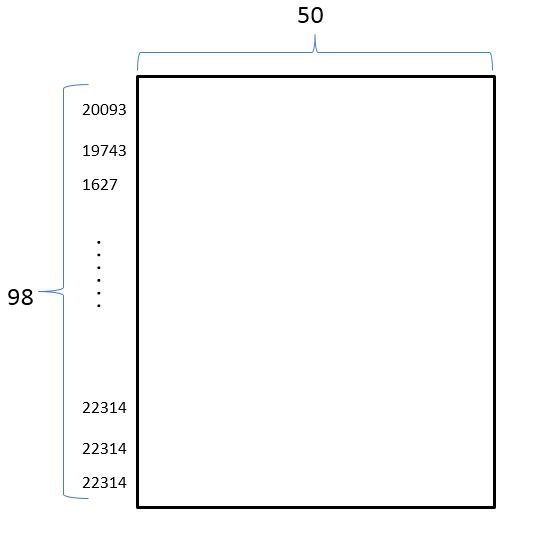
Raw_Example(label=3, entity1=PosPair(first=12, last=12), entity2=PosPair(first=15, last=15), sentence=[20093, 19743, 1627, 5836, 587, 9402, 10812, 9031, 1434, 10201, 1210, 1583, 4607, 13862, 1326, 6828])
最终一个句子被表示为一个二维矩阵(也就是word2vec):
文中的亮点操作1是:
词特征:考虑了实体的上下文词
句子:
"The system as described above has its greatest application in an arrayed <e1>configuration</e1> of antenna <e2>elements</e2>."
实体1的词特征:实体1的上一个词与下一个词configuration上一个词 arrayed ,下一个词of
实体2的词特征:实体2的上一个词与下一个词elements上一个词antenna ,下一个词<pad>(没有下一个词用特殊词<pad>来表示)
用数字表示:
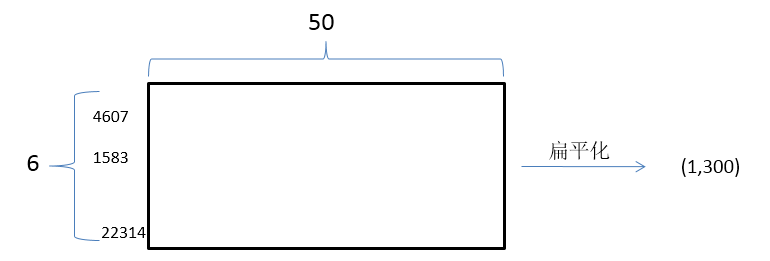
entity1_context:[4607, 1583, 13862]
entity1_context:[6828, 1326, 22314]
lexical_feature:[4607, 1583, 13862, 6828, 1326, 22314]
最终词特征的向量化表示就是:
文中的亮点操作2是:
位置特征:每个词离实体的相对位置

数字化表示就是:
entity1_posittion: [49, 50, 51, 52, 53, 54, 55, 56, 57, 58, 59, 60, 61, 62, 63, 64 ,……, 122]
entity2_posittion: [46, 47, 48, 49, 50, 51, 52, 53, 54, 55, 56, 57, 58, 59, 60, 61 ,……, 122]
向量化表示就是:

神经网络输入:词向量结合句子特征与位置特征构成卷积神经网络的最终输入
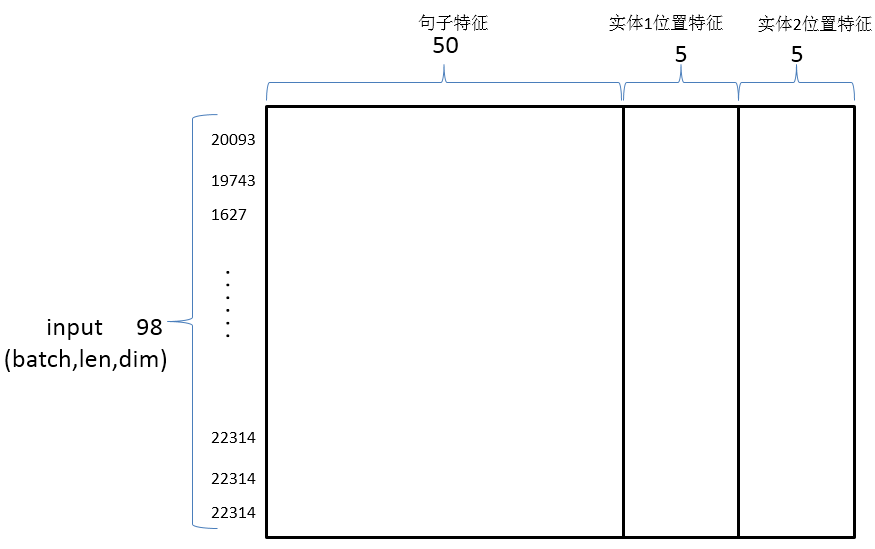
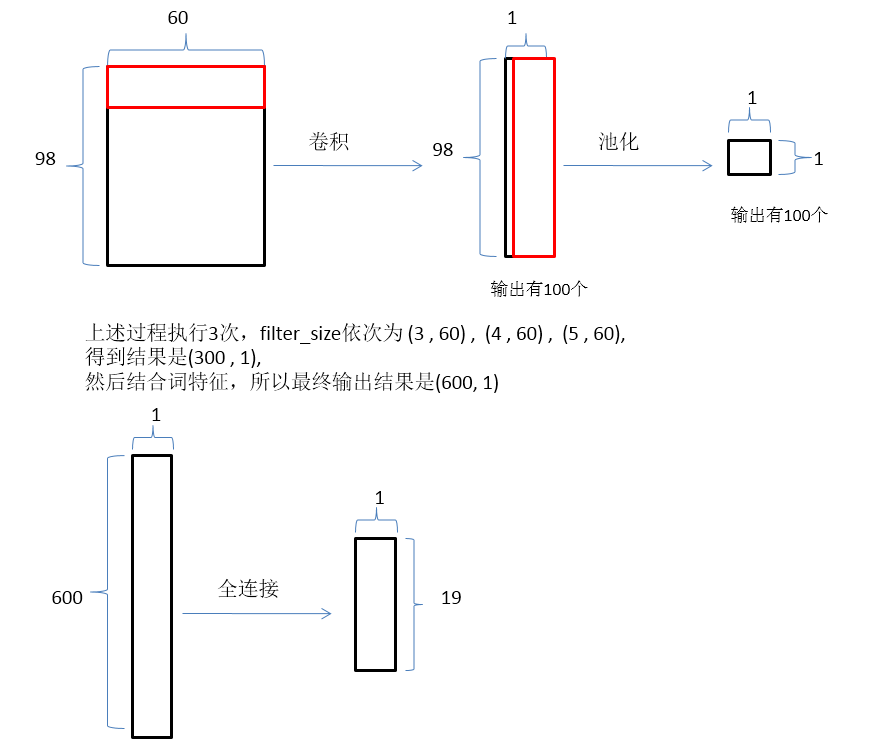
神经网络前向传播:
实验结果:
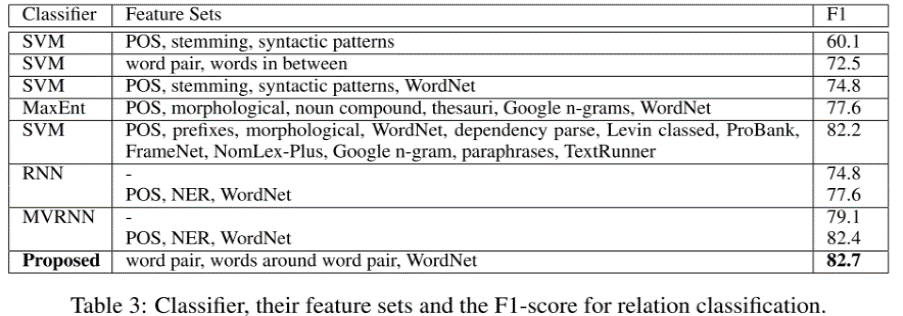 从实验结果可以看出,用作者提出的神经网络结构进行关系抽取的效果比传统的方法要好。
从实验结果可以看出,用作者提出的神经网络结构进行关系抽取的效果比传统的方法要好。